Conveyor rollers are an essential component of the manufacturing process that work as part of a unit to transport products or even loose bulk materials like coal, sand, or iron ore. Conveyor rollers are logically thought of as material-handling components with a cylindrical shape. Conveyor rollers are supported by a carrying structure that is propelled by a chain, a belt, or gravity. Additionally, there are drive rollers which have an integrated motor to motorize roller conveyors, eliminating the need for an additional drive unit; in this instance, materials are transported by a conveyor belt, which loops around pulleys and rollers. Read More…
Harwood Rubber Products provides top quality rubber rollers and a variety of custom products. We are capable of producing a great diversity of rolls and coverings for a broad customer base.

Since 1948, REDCO Rubber Engineering & Development has been manufacturing rubber rollers, idler rolls and conveyor rollers. We serve industries such as computers, printers and paper handling.

Our guide rollers are made from the highest quality materials in the industry. We take pride in adhering to our company values, like integrity and honesty. As a family owned and operated company, we like to treat customers like our own family. We will always look for the best prices and the prefect solution. Give us a call today to see how we can help you meet your goals!
TPC, Inc. is a dedicated and trusted manufacturer of rollers. We manufacture rollers in all shapes, sizes, designs, and colors to meet the needs of our customers and keep their process moving. Our team of experts is dedicated to the production and innovation of our products. As a result, TPC, Inc.’s custom-fit solutions are perfected for customers of all industries.
Since 1979, Uniflex has been a leading manufacturer of urethane products. We provide high-quality urethane rollers and urethane castings, as well as urethane molded products available in an array of colors. Uniflex offers customized body blocks and engine components for the automotive industry. Our team is dedicated to advancing our company and raising industry standards.
More Conveyor Roller Manufacturers
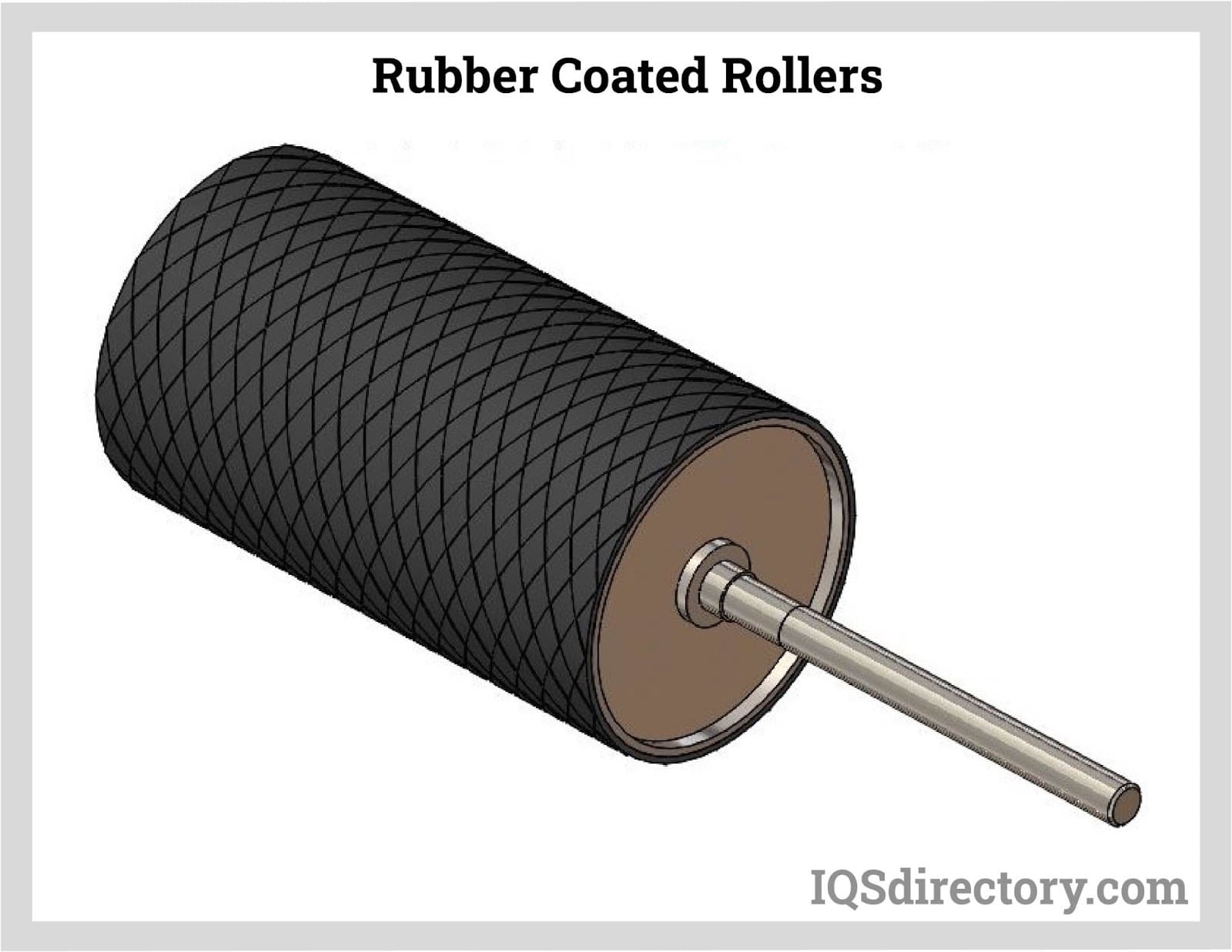
Conveyor rollers are essential components in modern material handling and automation systems, offering efficient movement of products and materials across manufacturing, packaging, distribution, and logistics facilities. These rollers can be fabricated from a range of materials, including plastic conveyor rollers, aluminum conveyor rollers, and steel conveyor rollers, each chosen for specific performance characteristics such as strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. To further improve the performance, durability, and safety of conveyor systems, many rollers are finished with a rubber coating or are manufactured as rubber rollers from the outset.
Rubber-coated conveyor rollers provide increased grip and traction between the roller surface and the conveyor belt or the product being transported. This enhanced friction is especially critical in preventing belt slippage and product shifting—common concerns in high-speed manufacturing lines, food processing, pharmaceutical packaging, and e-commerce order fulfillment centers. In addition, the use of non-marking rubber coatings ensures that sensitive or easily blemished goods, such as printed packaging or delicate electronics, are protected from surface marks and damage during handling.
How Conveyor Rollers Work
Understanding the mechanics of conveyor rollers is essential for optimizing your conveyor system design and minimizing downtime. A conveyor roller supports and guides the conveyor belt, which forms a continuous loop around pulleys located at the feed point (where materials are loaded) and the discharge point (where materials are unloaded). The conveyor belt moves materials efficiently from the loading area to designated unloading stations, streamlining internal logistics and reducing manual handling.
The conveyor belt system is divided into two main sections:
- Carry Section (Upper Section): This is the outward-facing segment of the belt, responsible for transporting products from the feed to the discharge point. The carry section is often subject to the highest wear and requires rollers capable of supporting both the load and the dynamic forces of movement.
- Return Section (Lower Section): After materials are discharged, the empty belt returns to the feed point via the return section. Conveyor rollers in this section support the belt’s return journey, helping maintain tension and alignment.
Strategically placed conveyor rollers ensure stable support, smooth belt tracking, and minimal energy loss throughout the conveyor’s operation. Advanced designs may integrate idler rollers, impact rollers, and guide rollers to further optimize performance in demanding environments.
Types of Conveyor Rollers
When selecting the right conveyor roller for your application, it’s important to understand the various types and their unique operational advantages. Different conveyor roller systems are engineered to meet specific requirements for load capacity, speed, environment, and automation level.
Chain-Driven Conveyor Rollers
Chain-driven conveyor rollers are commonly deployed for heavy-duty material handling applications, such as automotive assembly, pallet transport, and industrial manufacturing. These rollers are driven by chains that link directly to a power source, ensuring reliable torque transmission even under substantial load conditions.

There are two primary types of chain-driven roller conveyors:
- Roll-to-Roll Chain Drives: Power is transferred sequentially from one roller to the next via interconnected chains. This design is ideal for applications requiring synchronized movement of heavy loads, such as pallets, drums, or large containers.
- Tangential Chain Drives: In tangential chain roller conveyors, a single chain runs beneath the rollers, engaging each roller through a continuous hold-down region. While not as powerful as the roll-to-roll variant, this system enables longer conveying paths and is suitable for medium to heavy-duty use in warehouses and distribution centers.
Key advantages of chain-driven conveyor rollers include their ability to operate in harsh environments, manage irregularly shaped loads, and withstand exposure to oil, dust, and debris. If you’re comparing chain-driven roller conveyors vs. belt-driven rollers for your facility, consider the load weight, throughput, and the potential for abrasive contaminants.
Belt-Driven Conveyor Rollers
Belt-driven conveyor rollers are among the most versatile solutions in material handling, supporting a broad range of product types, sizes, and weights. In these systems, a belt (either flat or V-shaped) runs beneath the rollers, delivering rotational force to each roller and enabling controlled, consistent movement of goods.

Multiple configurations of belt-driven roller conveyors are available to match your production or distribution needs:
- Live Roller Conveyors: Each roller is powered by the belt, allowing precise control over product flow. These systems are ideal for operations that require accumulation, product sorting, or integration with automated controls.
- Curved Roller Conveyors: Designed to transport items around bends or corners, these systems use straight or V-shaped belts and often feature elevated rollers to accommodate oversized loads. Curved conveyors are frequently found in packaging, order fulfillment, and airport baggage handling.
- Reversible and Accumulation Systems: Belt-driven rollers can be engineered for bi-directional movement, product buffering, and temporary storage zones, optimizing workflow flexibility in high-volume environments.
Belt-driven roller conveyors are often chosen over ordinary flat belt conveyors when precise product positioning, smooth transfer, or gentle handling is required. They are especially useful for moving medium to large products that must remain dry, clean, and undamaged during processing or shipment.
Gravity Conveyor Rollers
Gravity conveyor rollers utilize the force of gravity to move products down a slight incline or along a horizontal path with minimal manual intervention. These rollers are not powered and are commonly used for loading docks, assembly lines, and packaging stations where products need to be transferred short distances quickly and efficiently. Gravity roller conveyors offer a cost-effective, low-maintenance solution for businesses seeking to optimize workflow with minimal energy consumption.
Motorized and Accumulation Conveyor Rollers
For automated facilities and smart warehouses, motorized conveyor rollers (also known as drum motors or powered rollers) integrate electric motors within the roller shaft. These advanced rollers deliver precise speed, torque, and zoning for accumulation, buffering, and merging processes. Accumulation conveyor rollers are instrumental in optimizing product flow, preventing bottlenecks, and supporting just-in-time inventory strategies.
Specialty Conveyor Rollers and Coatings
Beyond standard designs, specialty conveyor rollers are available to address unique application requirements:
- Rubber-Coated Rollers: Offer improved grip and product protection in applications such as glass manufacturing, food processing, and electronics assembly. Non-marking options ensure that finished goods maintain pristine surfaces.
- Stainless Steel Rollers: Engineered for washdown environments and cleanrooms, these rollers resist corrosion and contamination, making them ideal for pharmaceutical or dairy processing facilities.
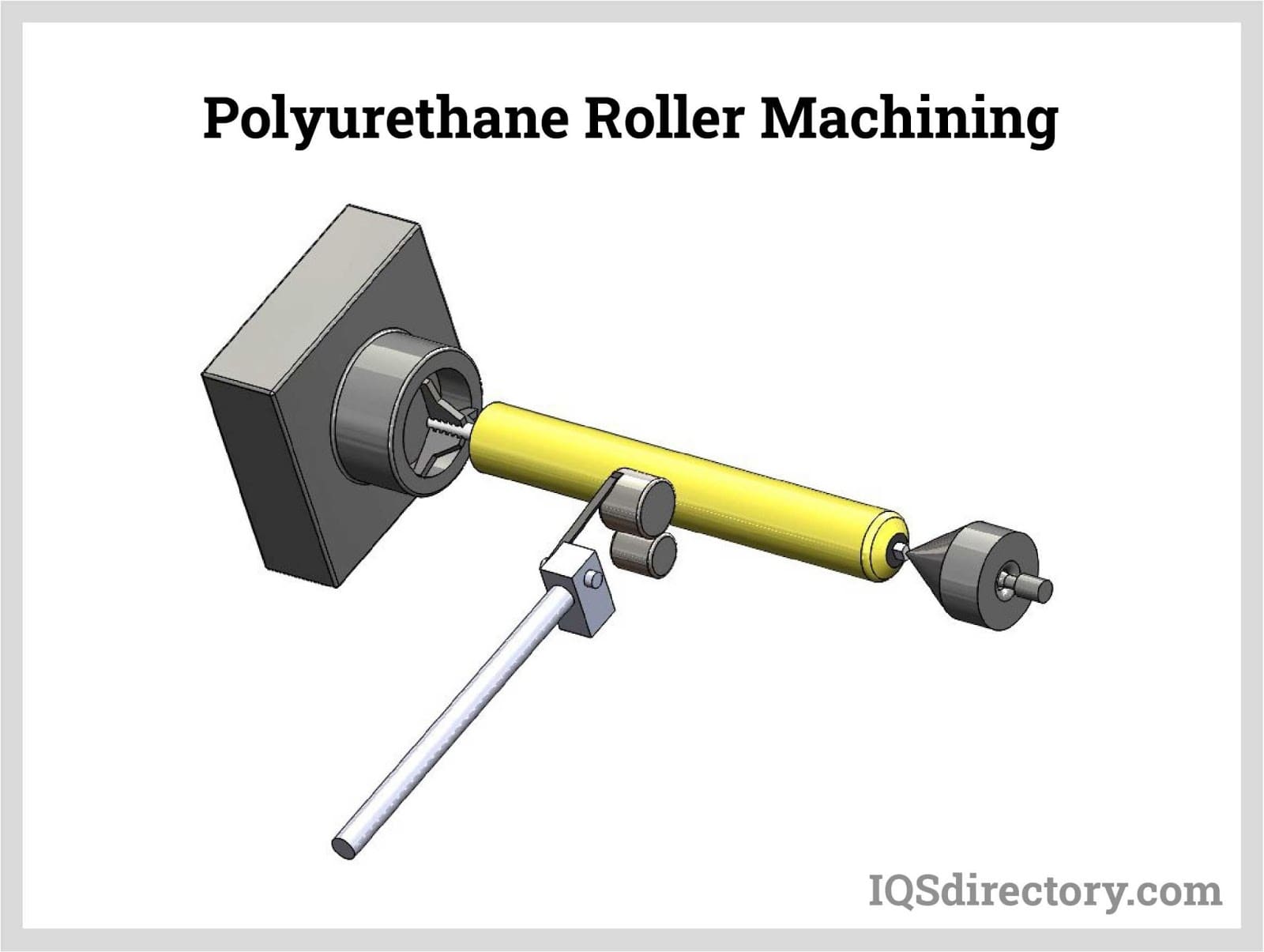
- Polyurethane-Coated Rollers: Provide high abrasion resistance, chemical stability, and quieter operation, frequently used in packaging, printing, and high-speed sortation systems.
- Grooved and Flanged Rollers: Enhance belt tracking and product alignment, reducing downtime due to misfeeds or jams.
Benefits of Conveyor Rollers
Investing in the right conveyor roller system can deliver a wide range of operational and business benefits:
- Modular design enables scalability and customization, providing flexible solutions for evolving material handling requirements.
- Simple installation, reliable operation, and minimal maintenance reduce total cost of ownership and maximize equipment uptime.
- Affordable method for moving products throughout production, warehousing, and distribution processes, reducing labor costs and improving throughput.
- Significantly decreases manual handling, enhancing workplace safety and reducing the risk of injuries or product damage.
- Compatible with both powered and non-powered systems, allowing seamless integration into existing workflows or automated environments.
- Curved roller sections, spurs, and custom options enable efficient routing of products through complex facility layouts.
- Rubber rollers and rubber-coated options provide soft, non-slip surfaces for superior traction, shock absorption, and product protection.
- Rubber-coated rollers absorb operational stresses, extending the service life of conveyor components and reducing maintenance costs.
- Uniform weight distribution across the roller surface minimizes concentrated pressure points, reducing product deformation and conveyor belt wear.
- Specialty coatings (such as FDA-approved, anti-static, or high-temperature) are available for demanding applications, including food processing, electronics, and chemical manufacturing.
Key Considerations When Selecting Conveyor Rollers
Choosing the most suitable conveyor roller for your facility requires careful evaluation of multiple factors. Here are some essential questions to ask when specifying or purchasing conveyor rollers:
- What is the maximum load weight and product size to be conveyed? Calculating the load rating ensures that rollers provide adequate support and durability.
- What is the required speed and throughput? Higher speeds may necessitate specialized bearings, coatings, or motorized rollers to prevent premature wear.
- Will the conveyor operate in harsh, wet, or sanitary environments? Material choice (such as stainless steel or coated aluminum) and roller design should match environmental demands.
- Is noise reduction a priority? Selecting rollers with polyurethane or rubber coatings can significantly reduce operational noise in customer-facing or quiet workspaces.
- What level of automation or accumulation is required? Motorized and accumulation rollers enable advanced product flow control and integration with warehouse management systems (WMS).
- Are there specific industry or safety regulations to meet? FDA, USDA, and CE compliance may be necessary for food, pharmaceutical, or export applications.
- What are the maintenance and replacement protocols? Opt for modular systems and easily accessible components to minimize downtime and simplify part replacement.
Looking to optimize your conveyor system for maximum efficiency? Contact a conveyor roller expert today to discuss your application, industry requirements, and unique challenges.
Common Applications of Conveyor Rollers
Conveyor rollers are found in virtually every sector that requires efficient, reliable movement of goods. Key application areas include:
- Manufacturing: Assembly lines, machine feeding, automotive production, and electronics assembly all leverage conveyor rollers for smooth, continuous material flow.
- Warehousing and Distribution: Automated sorting, order fulfillment, and cross-docking operations depend on conveyor roller systems for high-speed, accurate product routing.
- Food and Beverage Processing: Hygienic conveyor rollers move raw and packaged foods with minimal contamination risk, supporting strict sanitation standards.
- Pharmaceutical and Medical: Cleanroom-compatible rollers enable the safe handling of sensitive products, medical devices, and packaging.
- Logistics and Parcel Handling: Airports, post offices, and courier hubs use conveyor rollers for baggage, mail, and parcel sortation.
- Mining and Bulk Material Handling: Heavy-duty chain-driven rollers transport ores, aggregates, and raw materials in rugged environments.
- E-commerce and Retail: High-volume fulfillment centers rely on motorized and accumulation rollers to manage dynamic order streams and rapid dispatch.
Frequently Asked Questions: Conveyor Rollers
What are the main types of conveyor rollers?
The primary types include gravity rollers, belt-driven rollers, chain-driven rollers, motorized rollers, and specialized options such as rubber-coated or stainless steel rollers. Each type offers unique benefits for different industries and applications.
How do I determine the right roller material for my conveyor system?
Consider the operating environment, product type, load weight, and required cleanliness. Steel rollers excel in heavy-duty or abrasive settings; plastic and aluminum are suited for lightweight or corrosive environments; while rubber- or polyurethane-coated rollers offer enhanced grip and product protection.
What is the difference between powered and non-powered conveyor rollers?
Powered (motorized) rollers use electric motors or external drives to move products automatically, enabling advanced automation and accumulation. Non-powered (gravity) rollers rely on manual push or gravity to move items, making them cost-effective for simple, low-throughput operations.
How can I reduce noise and vibration in my conveyor system?
Choose rollers with soft rubber or polyurethane coatings, use precision bearings, and ensure proper alignment. Specialty noise-reducing rollers are available for sensitive environments such as hospitals or offices.
Can conveyor rollers be customized?
Yes, most manufacturers offer a range of customization options, including roller diameter, length, coating type, bearing style, and shaft configuration. Custom rollers can be designed for unique loads, environments, or automation requirements.
Choosing the Proper Conveyor Roller Manufacturer
To ensure the most positive outcome when purchasing conveyor rollers from a conveyor roller manufacturer, it is crucial to compare multiple manufacturers to find the best fit for your application, budget, and industry standards. Our comprehensive conveyor roller directory allows you to research and evaluate at least five top-rated manufacturers, each with a detailed business profile highlighting their expertise, certifications, and production capabilities.
When exploring conveyor roller suppliers, consider the following:
- Experience and Industry Focus: Does the manufacturer have a proven track record in your industry (e.g., food processing, logistics, heavy manufacturing)?
- Product Range and Customization: Can they supply the specific roller type, size, and coating you require? Are custom engineering and prototyping available?
- Quality Assurance and Compliance: Do their products meet relevant standards (ISO, FDA, CE) and undergo rigorous quality control?
- Lead Times and Inventory: What are their typical lead times, and do they maintain stock for rapid replacement or expansion?
- Technical Support and After-Sales Service: Will you have access to engineering advice, installation guidance, and maintenance resources?
- Pricing and Value: How do their costs compare, factoring in product quality, warranty, and total cost of ownership?
Each conveyor roller manufacturer in our directory includes a direct contact form, enabling you to request quotes, technical documentation, or schedule a consultation. Use our proprietary website previewer to assess their specialties and capabilities, then leverage our unified RFQ (Request for Quote) form to reach multiple vendors simultaneously. This streamlined process ensures you receive competitive bids and comprehensive information, empowering you to make informed purchasing decisions.
Ready to take the next step? Compare leading conveyor roller manufacturers now or request a quote for your project to receive tailored recommendations and expert support.
Whether you’re upgrading an existing conveyor, designing a new automated material handling system, or seeking specialized roller solutions for your industry, expert guidance is available. Contact us today to discuss your unique requirements, request samples, or schedule a site assessment with a conveyor roller specialist.







 Rubber Extrusions
Rubber Extrusions Rubber Molding
Rubber Molding Rubber to Metal Bonding
Rubber to Metal Bonding Rubber Tubing
Rubber Tubing Vibration Absorbers
Vibration Absorbers Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services